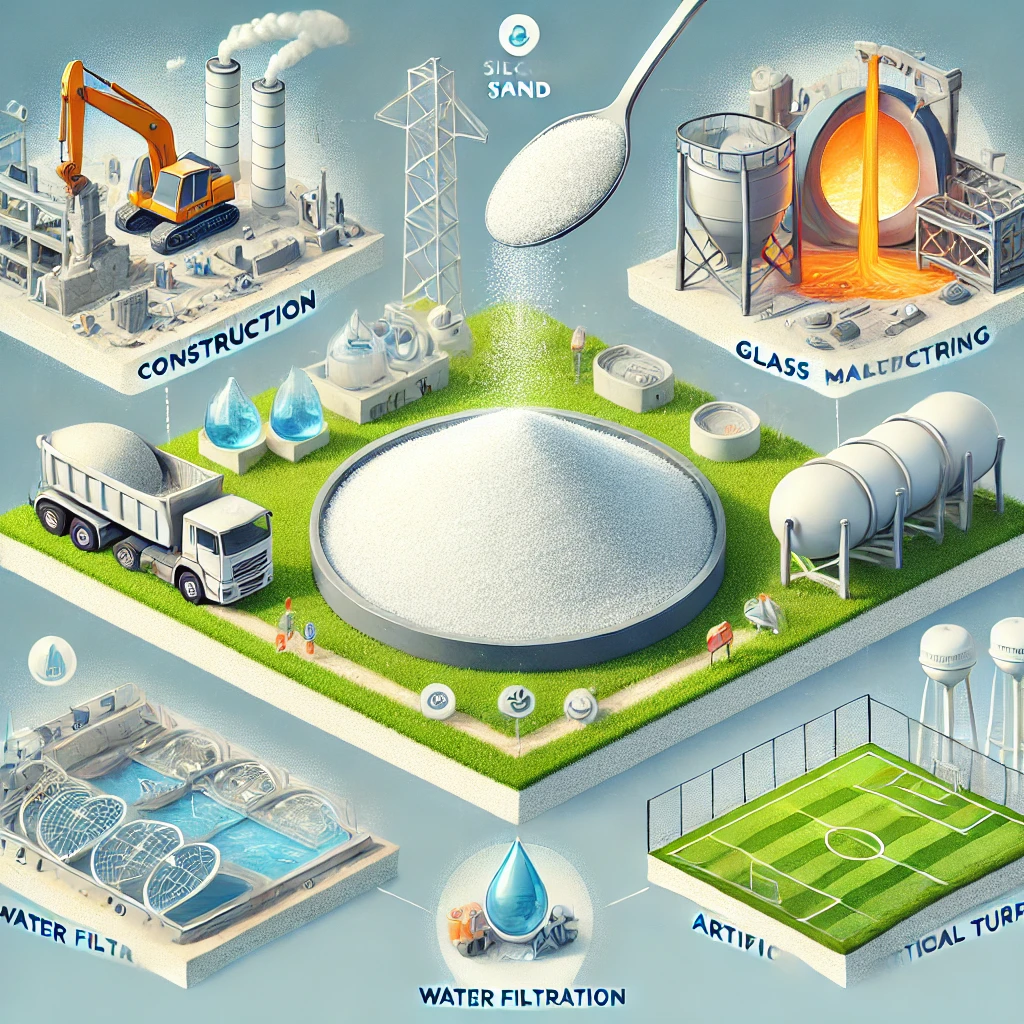
Silica sand and quartz sand are often used interchangeably in industrial and commercial settings due to their similar composition, but they have distinct differences that affect their applications and performance. Understanding these differences is crucial for industries such as construction, glassmaking, filtration, and more.
What Is Silica Sand?
Silica sand, also known as industrial sand, is a naturally occurring material composed mainly of silicon dioxide (SiO₂). It is derived from quartz but includes other mineral impurities such as feldspar, clay, and iron oxides. Silica sand is widely used in various industries due to its unique properties, such as high silica content, chemical inertness, and uniform particle size.
Common Uses of Silica Sand:
- Glass Manufacturing: Silica sand is a primary ingredient in the production of glass, including flat glass, container glass, and fiberglass.
- Construction: Used as a raw material for concrete, mortar, and paving materials.
- Foundries: Essential for mold and core making in metal casting.
- Filtration: Plays a key role in water filtration systems.
- Recreational Use: Found in playgrounds, golf courses, and sports fields.
What Is Quartz Sand?
Quartz sand is a subset of silica sand composed almost entirely of pure quartz grains. It is derived from the mineral quartz, which is one of the hardest minerals on Earth. Quartz sand typically has a higher purity level compared to silica sand and is less likely to contain impurities such as clay or organic materials.
Common Uses of Quartz Sand:
- Electronics: High-purity quartz is used in the production of silicon wafers for semiconductors.
- Solar Panels: Essential for the production of photovoltaic cells.
- Specialty Glass: Used in applications requiring high clarity and thermal resistance, such as lenses and laboratory equipment.
- Chemical Production: Acts as a raw material in the manufacturing of silicon-based chemicals and silicones.
Key Differences Between Silica Sand and Quartz Sand
| Feature | Silica Sand | Quartz Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | Contains impurities like clay and feldspar | Higher purity with minimal impurities |
| Applications | Broad industrial applications | Specialized applications in electronics |
| Color | Typically off-white, beige, or tan | Clear to translucent |
| Price | Generally less expensive | Higher cost due to purity and scarcity |
How to Choose the Right Sand for Your Needs
Choosing between silica sand and quartz sand depends on the specific requirements of your project or industry. Here are some factors to consider:
- Purity: For applications requiring high chemical or thermal stability, quartz sand is ideal.
- Cost: If cost is a major factor and high purity is not essential, silica sand is more economical.
- Application: For general construction or filtration, silica sand suffices, while quartz sand is better suited for electronics and specialty glass.
Conclusion
While silica sand and quartz sand share similarities in composition, their differences in purity, applications, and cost make them suitable for distinct uses. Understanding these differences helps industries select the right material to optimize performance and cost-efficiency. Whether you’re manufacturing glass, constructing buildings, or working in advanced electronics, knowing the unique properties of these sands can make all the difference.
By comparing these two materials, you can ensure your project gets the ideal type of sand for the best results. For more information about silica sand and its applications, visit our silica sand resource page.